Scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 2024 in Orlando, USA
June 21-24 2024
Daphné Bernard, one of our PhD students, was in Orlando for one of the world's largest diabetes congress organized by the American Diabetes Association (ADA). She presented her project, which focuses on the impact of Myokine X on adipose tissue of a type 2 diabetes rodent model. This well-known scientific session was a great opportunity to highlight our latest work on the effects of our “Myokine X”.
As you may know, our team discovered that:
- a crosstalk exists between the muscle and the pancreas in a context of type-2 diabetes
- the muscle’s secretome (the triceps in particular) during resistant exercise has beneficial effects on the pancreas. The team especially puts forward the positive effects of one myokine, the Myokine X, on β-cell survival and function.
In this context, Daphné Bernard’s PhD project aims to study the effect of the Myokine X on adipose tissue - pancreas crosstalk in the context of type-2 diabetes. This study is even more relevant since one of type-2 diabetes’ complication is the energy imbalance that induces adipose tissue dysfunction causing disease worsening and complications. Thus, it is necessary to find new therapies targeting adipose tissue.
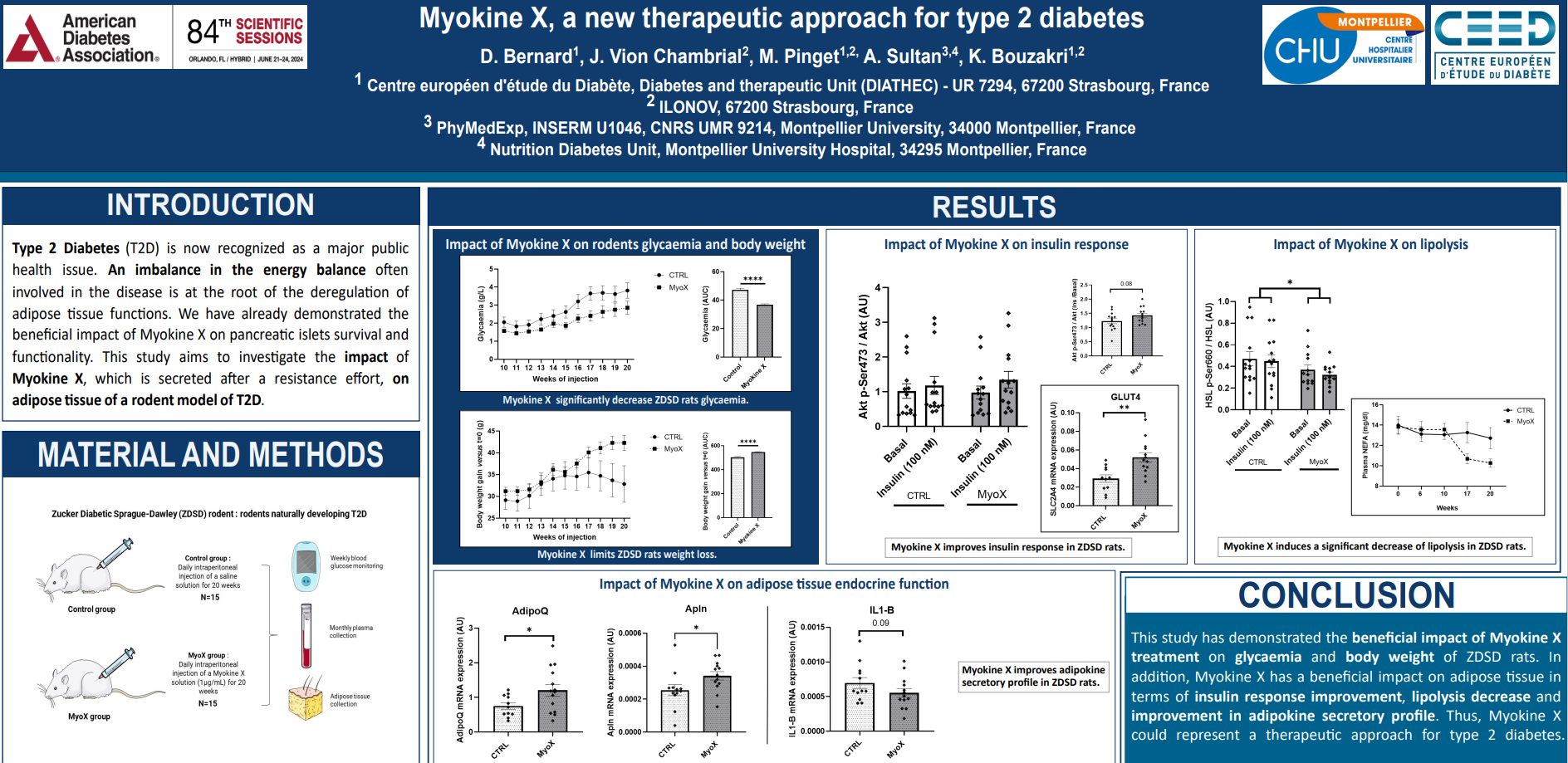
Abstract
Myokine X, a new therapeutic approach for type 2 diabetes
D. Bernard1, J.Vion-Chambrial2, M. Pinget1,2, A. Sultan3,4, K. Bouzakri1,2
1 Centre européen d’étude du Diabète, Unité Diabète et Thérapeutique (DIATHEC) – UR7294, 67200 Strasbourg, France
2 ILONOV, 67200 Strasbourg, France
3 PhyMedExp, INSERM U1046, CNRS UMR 9214, Université de Montpellier, 34000 Montpellier, France
4 Département Nutrition-Diabète, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Montpellier, 34295 Montpellier, France
In a context of hyperglycaemia and excess of fatty acid intake leading to the disease, adipose tissue functions are dysregulated. We have already demonstrated the beneficial impact of Myokine X on pancreatic islets survival and functionality. This study aims to investigate the impact of Myokine X, which is secreted after a resistance effort, on adipose tissue of a rodent model of T2D.
Zucker Diabetic Sprague-Dawley (ZDSD) rat, naturally developing type 2 diabetes, received a daily peritoneal injection of either a saline solution (control group) or a Myokine X solution at 1 µg/mL for 20 weeks. Animals were sacrificed at the end of the 20 weeks and adipose tissue was analysed by western blotting or by qPCR for gene expression. The significance of the data was assessed using Student's t test to compare two conditions. When several factors were present, two-way ANOVAs were performed.
Myokine X treatment revealed (i) an impact on insulin pathway with an increase of 16.5% of Akt p-ser473 phosphorylation capacity, with simultaneously a significant increase of 78% for GLUT4 mRNA expression, (ii) a significant decrease of HSL phosphorylation on ser660 (-24%), (iii) an increase of adipokines mRNA expression with beneficial impact on insulin pathway.
This study shows that Myokine X treatment had a positive impact on adipose tissue in a rodent model of T2D, in terms of insulin sensitivity improvement, HSL activation decrease and improvement of adipose tissue secretion, adipokines. Thus, Myokine X could represent a therapeutic approach for T2D treatment.